Custom Exception, Handler 구현하기
비즈니스 로직을 구현하다 보면, 정상적인 흐름도 존재하지만 Exception을 발생시켜야 하는 상황이 생깁니다.
또한 I/O Exception 등을 처리하지 않게 된다면 500 에러가 발생하므로 잡아주는 작업이 필요합니다.
이번 시간에는 Exception을 보다 효율적으로 핸들링할 수 있도록 Custom Exception을 만들고 Exception을 처리할 수 있는 Exception Handler를 구현해보겠습니다.
Custom Exception 구현
보통의 경우에는 Exception을 잡아서 Response를 만드는 과정이 필요합니다.
예를 들어, 404 응답을 해야되는 경우,
1
2
3
4
5
try {
return ResponseEntity.ok(readUserUseCase.getUserById(id));
} catch(NotFoundException e) {
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
와 같이 Exception을 처리하면서 Response를 구현합니다.
만약 Exception 안에 Response가 존재한다면 어떨까요?
Exception 그 자체가 Response가 될 수 있기 때문에, Exception 마다 다른 Response를 만들어줄 필요가 없을 것입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
try {
return ResponseEntity.ok(readUserUseCase.getUserById(id));
} catch(CustomException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(e.getStatus()).body(e.getBody());
}
이는 Exception을 잡아줄 때 새로운 Response를 생성하는 것보다 더 추상적이며 재사용 가능한 코드를 만들어 줄 것입니다.
따라서, Response할 정보를 미리 가지고 있는 CustomException을 구현해보겠습니다.
CustomException
1
2
3
4
5
6
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Getter
public class CustomException extends RuntimeException {
private final ErrorCode errorCode;
}
CustomException은 ErrorCode를 가집니다.
여기서 ErrorCode는 Response를 생성할 수 있는 정보를 가지고 있는 객체입니다.
따라서 CustomException을 생성할 때, 필요한 ErrorCode를 전달하도록 합니다.
ErrorCode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
@RequiredArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@Getter
public enum ErrorCode {
// 4XX
BAD_REQUEST(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.getReasonPhrase(), "The request is invalid or cannot be processed."),
UNAUTHORIZED(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value(), HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.getReasonPhrase(), "Your request could not be authorized."),
NOT_FOUND(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(), HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.getReasonPhrase(), "The requested resource was not found."),
// 5XX
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getReasonPhrase(),
"An internal server error occurred."),
private final int httpCode;
private final String httpMessage;
private final String moreInformation;
}
ErrorCode는 앞서 말했던 것처럼 Error Response를 만들 수 있게, 필요한 정보들을 담고있어야 합니다.
저는 HTTP status code와 간단한 message, 조금 더 상세한 정보를 담을 수 있도록
- httpCode
- httpMessage
- moreInformation
으로 구성해보았습니다.
여러 인스턴스를 생성할 필요가 없으므로, 싱글턴으로 Enum을 사용합니다.
사용 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
class ClientValidationService implements ValidateClientUseCase {
private final ReadClientPort readClientPort;
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public void validateClient(ValidateClientCommand command) {
readClientPort.findByClientId(command.clientId())
.filter(e -> e.isClientSecretMatched(command.clientSecret()))
.orElseThrow(() -> new CustomException(ErrorCode.UNAUTHORIZED));
}
}
사용 방법은 간단합니다.
만약 비즈니스 로직을 수행 중 Exception을 던져야 하는 상황이 발생하면, Response에 사용할 ErrorCode를 골라 CustomException을 던져주면 됩니다.
예시로, RestController에서 해당 CustomException을 잡아 Error Response가 가능할 것입니다.
하지만 이러한 방법은 항상 예외를 잡아주는 코드를 강제하게 됩니다.
그렇다면 예외만 던지면 알아서 Error Response를 만들어주는 방법은 없을까요?
Exception Handler 구현
Spring Web은 특정 Exception이 발생하면 미리 정한 Response를 응답하는 Handler를 구현할 수 있도록 @RestControllerAdvice를 제공합니다.
따라서 Exception을 매번 처리해줄 필요가 없어집니다.
RestControllerAdvice
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
@RestControllerAdvice
public class CommonExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class)
private ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleCustomException(CustomException e) {
return handleCustomExceptionInternal(e.getErrorCode());
}
@ExceptionHandler(Excpetion.class)
private ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleCustomException(CustomException e) {
return handleCustomExceptionInternal(e.getErrorCode());
}
private ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleCustomExceptionInternal(ErrorCode errorCode) {
ErrorResponse response = ErrorResponse.builder()
.httpCode(errorCode.getHttpCode())
.httpMessage(errorCode.getHttpMessage())
.moreInformation(errorCode.getMoreInformation())
.build();
return ResponseEntity.status(errorCode.getHttpCode()).body(response);
}
}
@RestControllerAdvice의 사용 방법은 위와 같습니다.
@ExceptionHandler를 통해 핸들링할 Exception을 정한뒤 핸들러를 구현합니다.
이 때 핸들러의 반환 값이 Response가 됩니다.
만약 특정 @RestController만 @RestControllerAdvice를 적용하고 싶거나, 도메인마다 다른 @RestControllerAdvice를 적용하고 싶은 경우는 어떻게 할까요?
이는 BasePackage 설정과 어노테이션을 통해 가능합니다.
BasePackage 설정은 다음과 같습니다.
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackages = ...)- 특정 패키지에 속한
@RestController에만@RestControllerAdvice를 적용합니다.
어노테이션을 통한 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
@RestControllerAdvice(annotations = ...)- 해당 어노테이션이 붙은
@RestController에만@RestControllerAdvice를 적용합니다.
이제 비즈니스 로직 수행 중, Error를 Response하고 싶다면 CutomException만 던져주면 모든 것이 해결되는 마법을 볼 수 있습니다!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
class ClientValidationService implements ValidateClientUseCase {
private final ReadClientPort readClientPort;
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public void validateClient(ValidateClientCommand command) {
readClientPort.findByClientId(command.clientId())
.filter(e -> e.isClientSecretMatched(command.clientSecret()))
.orElseThrow(() -> new CustomException(ErrorCode.UNAUTHORIZED));
}
}
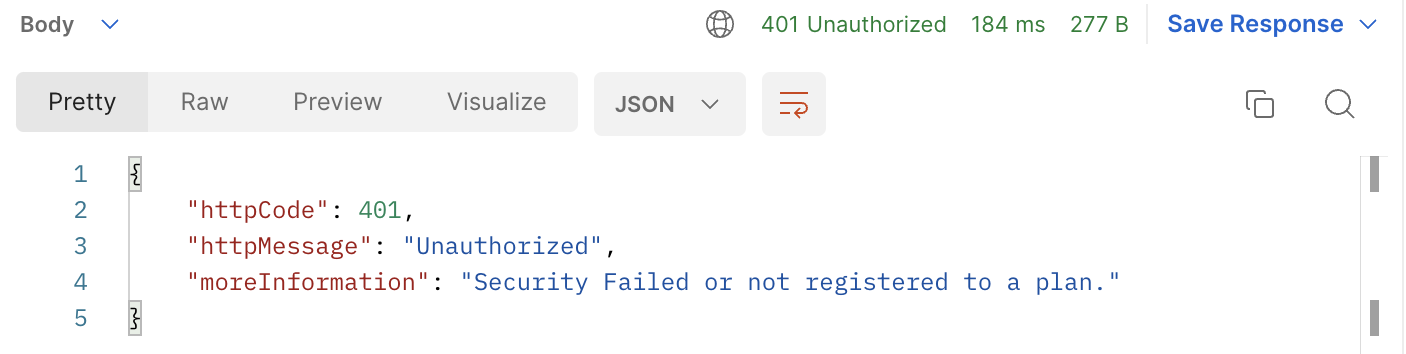
여기서 CustomException이 던져지면…
기대한 동작을 확인할 수 있습니다.